Is Your Attunity NonStop Solution for Data-sharing at End-of-Service-Life (EOSL)?
Share This!
 Copy link to clipboard
Copy link to clipboard Email link
Email link Print
Print
Easily Modernize and Expose Valuable Enscribe Data – Eliminate Data Silos with HPE Shadowbase
Several customers recently approached us looking for solutions to their remote data access/connection requirements. HPE Shadowbase software uses a data replication/integration architecture to meet these needs and has experience successfully deploying these solutions at a number of customer sites.
(Related Video Presentation at bottom of the page.)
Resolving this Challenge
In the past, companies accessed trapped data via remote clients. Unfortunately, this approach had several issues:
- Queries impacted several key components
- Production environment
- Network
- CPU resources
- Queries timed out and failed if the network was down or the production environment was inaccessible
Today, these companies face a dilemma: “What do we do if our solution has gone End-of-Service-Life (EOSL)? Also, what about the future?” Answer: A proven and preferably original equipment manufacturer (OEM-provided) solution that leverages data replication capabilities to eliminate these past problems.
Let us examine why the following HPE Shadowbase architectures are popular and have significant advantages over alternative architectures, and which is best for you:
- Off-platform Replication
- HPE Shadowbase software transforms and replicates the customer’s trapped and siloed Enscribe, SQL/MP, and/or SQL/MX source data into a different remote target platform and database (e.g., to Linux/Oracle or Windows/SQL Server).
- The customer’s applications can then access the data locally through ODBC or JDBC interfaces.
- On-platform Replication
- HPE Shadowbase software transforms and replicates the customer’s trapped and siloed Enscribe source data on-platform (in the existing environment) into a SQL/MP or an SQL/MX database.
- Remote applications can then use, for example, ODBC/MX and JDBC, to access the NonStop-based SQL data.
- This architecture leverages the high availability of the NonStop platform to preserve data accessibility, and most closely matches the customer’s original remote data access/connection architecture.
Off-platform Replication Case Study: Large Steel Tubing Manufacturer
Situation
A large European steel tube manufacturer ran its online shop floor operations on an HPE NonStop Server. To exploit the currency and value of this online, trapped, and siloed data, the manufacturer periodically generated reports on Linux Servers using a customized application and connectivity tool that remotely queries the online NonStop Enscribe database and returns the results (Figure 1).
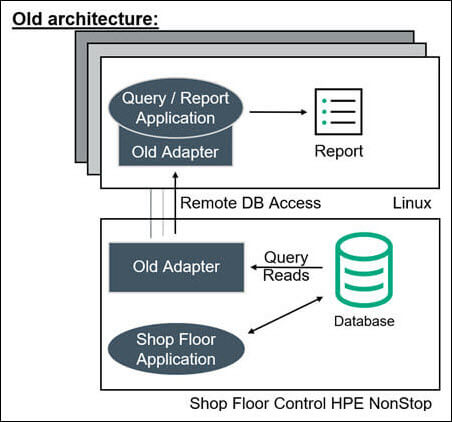
Figure 1 – Original Remote Query Architecture
Old Architecture
With this original architecture, every time a Linux query/report was run, processing on the NonStop Server was required, and as query activity increased, this workload started to significantly impact online shop floor processing. This impact was compounded due to the high volume of data transformation and cleansing required for converting the Enscribe data into a usable format for the reports. Periodically, the company needed to suspend the execution of reports due to these production impacts. In addition, the remote connectivity architecture was not very robust or scalable and was also susceptible to network failures, timeouts, and slowdowns when operating at full capacity. Since the data adapter used was nonstandard, the manufacturer could not access the data using standard ODBC and OLAP[1] tools to take advantage of new analytical techniques (such as DSS[2]). Furthermore, the company had a new requirement to share the OLAP analysis with the online NonStop applications in order to optimize shop floor control, which was completely impossible with the original solution. Therefore, a new architecture was required to address these issues and meet the new requirements.
Rearchitecting Operations
The manufacturer completely rearchitected its Linux-based querying/reporting application. Rather than remotely querying the NonStop Enscribe data each time a report runs, the data is replicated by HPE Shadowbase software in real-time from the Enscribe database to a copy of that database hosted on a Linux system. This architectural change only requires the data to be sent across the network once (when it is changed), instead of every time a query/report is run.
The raw Enscribe data is non-normalized and full of arrays, redefines, and data types that do not have a matching relational data construct (e.g., SQL data type). As part of the replication process, the non-relational Enscribe data is transformed and cleansed by HPE Shadowbase software into a relational format, and written to an Oracle RAC database. This architectural change only requires the data to be cleansed and/or normalized once when the data is changed, rather than every time a query/report is run.
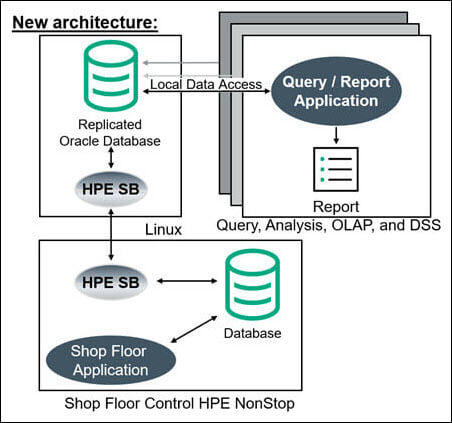
Figure 2 – The Manufacturer’s New Off-platform Replication Architecture Featuring Local Database Access
Since the data is now local to the Linux Servers and presented in standard relational format, it is possible to use standardized SQL data query and analysis tools (Figure 2). The benefit of achieving this level of integration cannot be overstated; the customer now has the full power provided by the analytical tools market to manipulate its raw information to achieve data intelligence.
In addition, HPE Shadowbase software allows the manufacturer to reverse replicate the OLAP results and share those results back with the NonStop applications to better optimize the shop floor manufacturing process. This integration dramatically improves shop floor control operations and avoids having to architect yet another interface.
Off-platform Replication Benefits
This new architecture completely resolves the issues with the old mechanism by decoupling the data access and transformation/cleansing process from the querying/reporting process, and by presenting the data locally on the Linux system in standard relational format:
- Querying/reporting and data transformation/cleansing impact on the production NonStop system is eliminated. Online data replication has much lower overhead than executing queries and performing data transformation/cleansing directly on the NonStop Enscribe database every time a query is executed. This architecture dramatically reduces the workload on the NonStop Server, avoids throughput and response time issues with the shop floor applications, and eliminates the periodic need to suspend running reports.
- Querying/reporting performance is dramatically improved. It is much faster to run queries and reports against an already transformed/cleansed local relational database using standard ODBC access, than it is to remotely access the NonStop Enscribe database and spontaneously perform the necessary data transformation/cleansing every time a query or report is executed.
- Querying/reporting application availability is improved. A local Linux copy of the database is used so that an outage of a network or a NonStop Server will not impact the querying/reporting applications.
- The shop floor application’s scalability is improved. A local database access is inherently more scalable than executing remote queries across a network, especially when removing the need for data transformation/cleansing on every query. Competition for resources on the NonStop Server is also greatly reduced by offloading workload to the Linux systems. In addition, the original architecture typically only allowed a single report to run at any one time (to minimize the impact on the NonStop production system). Now, with the data hosted on a Linux Oracle RAC database and the NonStop system out of the query loop, multiple reports and advanced analytics can be executed in parallel.
- Analytics and data value are improved. Transforming and cleansing the Enscribe data into relational format and storing it in a local relational database enables the use of standard ODBC database access. It also enables additional off-the-shelf querying/reporting tools to extract even more value from the data (including OLAP and DSS). The ability to share the OLAP analysis with the NonStop production applications using Shadowbase bi-directional data integration enables new uses for the data (in this case, to better optimize the shop floor manufacturing process).
On-platform Replication Case Study: Large Bank
Situation
A large bank operates one of the biggest ATM/POS networks in North America using BASE24™, running on HPE NonStop servers. BASE24 is a popular application used worldwide by banks for this purpose. If this ATM/POS service goes down, much of the region’s retail commerce would come to a halt. For example, at peak times this application services almost 2 million ATM/POS transactions per hour.
Old Architecture
The bank’s original architecture is similar to the manufacturer’s original architecture (see above). Off-platform applications running on Windows used a third-party API to access the on-platform Enscribe database, making it accessible as if it were a local, relational SQL database.
The API converted all of the hierarchical Enscribe data structures (fields, files) into SQL equivalents (columns, tables), and then provided queriable views against the underlying Enscribe database. Unfortunately, this third-party API went EOSL. The bank needed a new solution to replace this API.
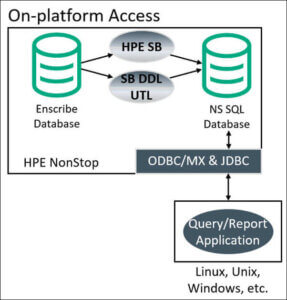
Figure 3 – The Bank’s New On-platform Replication Architecture Featuring Remote Database Access
Rearchitecting Operations
Shadowbase software is now used to transform and replicate the source Enscribe data into the desired on-platform target SQL structures (NonStop SQL/MX in this case). Remote applications then use standard ODBC or JDBC query tools, or client APIs, to remotely access the data in the SQL/MX database (e.g., via ODBC/MX).
The on-platform architecture is similar to the original architecture employed by the customer – only the remote query application client library changes – which can be very advantageous if the customer cannot easily accommodate or manage off-platform systems (e.g., Linux, Windows, Unix) and databases (e.g., Oracle, SQL Server, Db2®).
Additionally, keeping the database on the NonStop Server provides all of its inherent fault-tolerant availability benefits, including its unequaled NonStop SQL database query capabilities (e.g., for parallel processing provided by SQL/MX). Of course, when adding additional processing to the existing system, sizing and performance analysis should also be performed to ensure that the system capacity is adequate (otherwise, additional CPU or disk space may be needed).
On-platform Replication Benefits
The bank’s new architecture completely resolves the issues with the old mechanism by decoupling the data access and transformation/cleansing process from the querying/reporting process, and by locally presenting the data on a mission-critical system in standard relational format:
- Querying/reporting is simplified, faster, and functionality is greatly enhanced. Since the data is on a database that is accessible via ODBC/MX or JDBC, the querying/reporting database is accessible to groups outside of the NonStop team. This team can now offload these querying/reporting projects to other teams so that it can focus on improving NonStop operations for the bank’s production applications.
- This architecture offloads the reporting workload from the production Enscribe database into an on-platform, local SQL/MX database. Running queries directly on the production database creates unnecessary risks. For instance, an informed actor could inject malicious code into the query, and alter the Enscribe database in ways that the NonStop may not even detect. Since the data on the NonStop SQL database is updated immediately after a change is made to the production Enscribe database, both databases are synchronized (excluding the replication latency from asynchronous replication engines, which is typically negligible). This step enables remote data access for queries via ODBC/MX and JDBC.
- The bank can now create sophisticated, structured SQL queries and customized reports and dashboards, enabling associates to make informed decisions from customized reports and dashboards, enabling real-time business intelligence. Since the data is available to commodity applications, the bank can create anything from simple alerts to complex profit and loss statements.
- Transforming the data once simplifies this architecture and creates a local copy of the production database, which can be used as a DR backup in a difficult situation. The conversion from Enscribe File format into SQL/MX tables occurred only once on the same system, meaning the NonStop team was able to independently control and execute this project. The team did not need to transform the data to an off-platform system, which might entail complex transformations, and slower project turnaround, since multiple teams within the bank would need to collaborate. In a worst-case scenario (note, this is not recommended for a Disaster Recovery solution) where an Enscribe file is accidentally deleted or cannot be found, the team can look for the missing data in the SQL copy and recover it from there.
Summary
These case studies only scratch the surface of data replication’s potential. It can:
- Integrate disparate applications, such as an online production shop floor application with a reporting application.
- Eliminate data silos by exposing valuable data and enabling the creation of new business processes.
- Distribute data wherever it is needed with low overhead while it transforms and cleanses that data.
- Distribute data where it can easily be consumed by other applications (typically without requiring any application changes).
- And much, much more.[3]
Data replication is not only for providing a backup for business continuity, but also for moving data in real-time as required, in order to leverage its value wherever needed. Think about your valuable, yet isolated, data and consider how you could use data replication to unlock this value for competitive advantage and to build new solutions for your business.
Implementing these Shadowbase solutions is also very straight-forward, regardless if the data is being replicated NonStop/NonStop, NonStop/some other platform, or other configurations. Shadowbase software has powerful utilities to aid in the data format/schema conversions, for data cleansing, transformation, and filtering.
For more information, please watch our presentation or visit this case study, where a customer recently replaced an Attunity NonStop solution with Shadowbase software. If you have similar needs, please contact us or your HPE account team to discuss your requirements and timeline.
Footnotes
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is the technology behind many Business Intelligence (BI) applications. OLAP is a powerful technology for data discovery, including capabilities for limitless report viewing, complex analytical calculations, and predictive “what if” scenario (budget, forecast) planning.
- A Decision Support System (DSS) is a computerized information system used to support decision-making in an organization or a business. A DSS lets users sift through and analyze massive reams of data and compile information that can be used to solve problems and make better decisions.
- For more information, please see the Gravic white papers, HPE Shadowbase Streams for Data Integration, and HPE Shadowbase Streams for Application Integration.
Is your vendor solution for sharing data across platforms or applications going end-of-service-life (EOSL)?
Learn how to use HPE Shadowbase solutions to expose your valuable Enscribe siloed data using a data replication solution that provides significant advantages:
- Simplified Architecture – replace a remote CPU-intensive approach with local access to a replicated database
- Improved Response Times – dramatically reduce the impact of data query and reporting using local, not remote, data
- Reduced CPU Utilization – convert the query/reporting data once into the relational format needed, rather than each time the query/report is run
- Improved Query/Data Availability – eliminate slow or failed system or networking issues from preventing the applications from running
- Standardized Access – use the latest ODBC and JDBC interfaces, allowing for advanced SQL data access features and OLAP processing
- Exposed Siloed Enscribe Data – convert non-relational Enscribe data into standard SQL relational formats to expose data value
Presented by Paul Holenstein, Gravic EVP



